What is a DPF?

DPF stands for Diesel Particulate Filter.
Its purpose is to filter Diesel Particulate Matter (DPM), also known as soot, out of exhaust gasses.
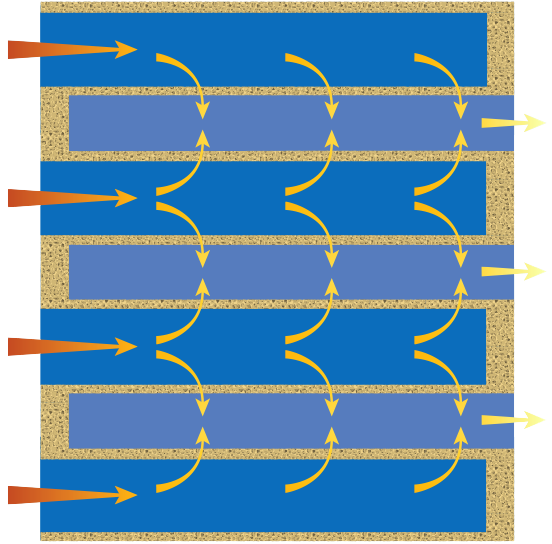
Exhaust gasses containing soot enter the DPF. The filter traps any matter larger than one micron, allowing gasses through.
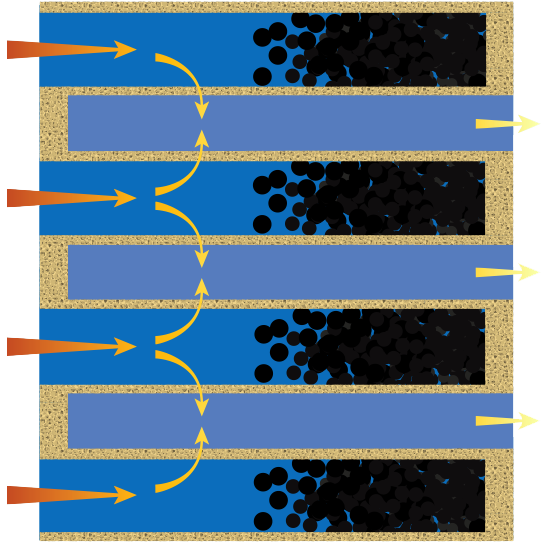
Over time, soot builds up in the DPF. Eventually, this causes back pressure detected by the Engine Control Unit (ECU) necessitating regeneration.
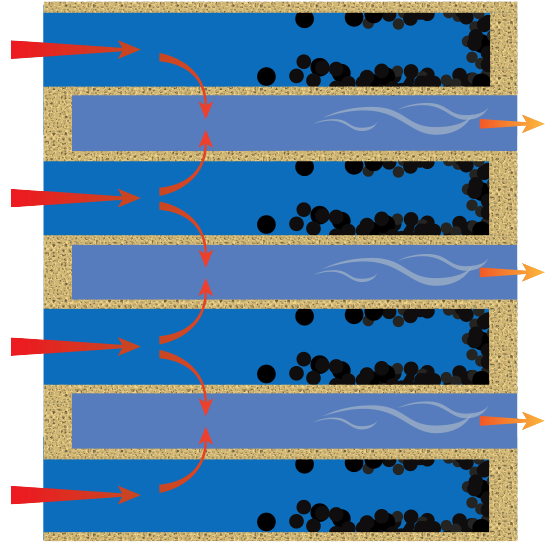
Regeneration (regen) requires high exhaust temperatures of 570°-750°C. Combining high temperatures and a unique mix of precious metals washcoat and substrate turns soot into ash. The DPF is now regenerated and ready for use.

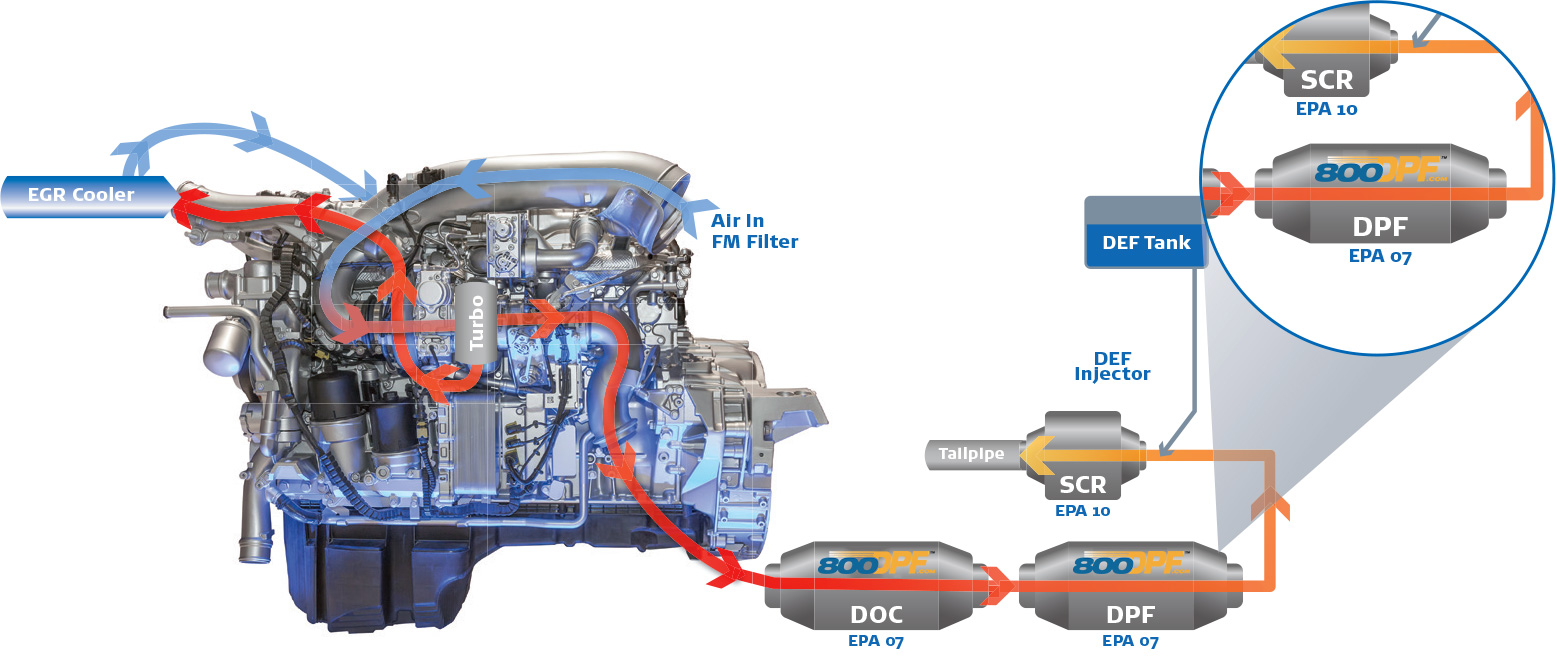
Passive
Automatic regen that occurs when the DPF reaches the correct exhaust temperatures.
Active
If a regen doesn’t complete a cycle, but sensors indicate DPF has reached capacity, an active regen occurs. The DPF dashboard light indicator will come on and the vehicle must continue to move to finish the cycle.
Manual
If an active regen can’t complete, typically due to short drive times, then a manual regen will be required in a shop.

