What is a DOC?
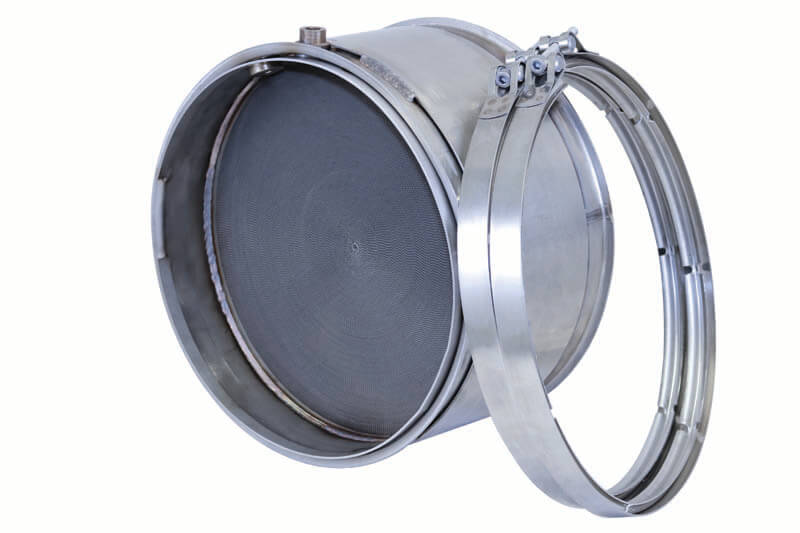

DOC stands for Diesel Oxidation Catalyst.
The DOC works in conjunction with the DPF by heating the exhaust going into the DPF so the exhaust is hot enough to burn the soot out of the DPF.

When an active or manual regen is required, the HC (hydrocarbon) injector adds a bit of fuel into the exhaust system.
The HC injector is also called the fuel doser or after treatment injector.
The dosed diesel goes onto the DOC, which, by catalytic reaction heats up the DPF.
Leaks in upstream pipe.
To see how leaks in upstream pipes affects proper DOC and DPF function, we just need to look at the physics. Take a look at the Ideal Gas Law. In a manufactured structure such as a truck exhaust system, there are constants. Gas volume (V), gas mass (n), and gas constant (R) are predetermined by the exhaust makeup. However, pressure (P) and temperature (T) are variables in this system. If the pressure is low due to leaks in the upstream pipe, then the temperature will, by the laws of physics, be lower too. Regen cannot take place if the system can’t get up to temperature. Possible leak sources include the turbo, the EGR cooler, pipes, at the clamps, and bellows.
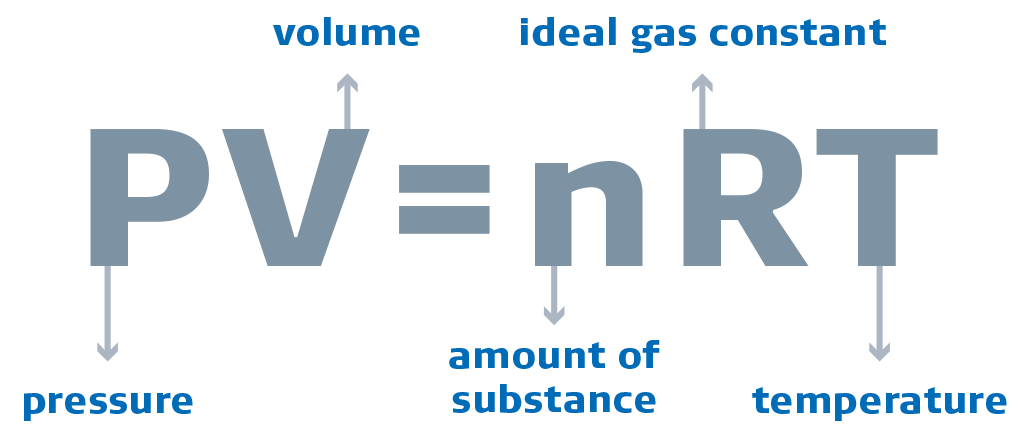
Common Upstream Failures
The HC injector clogged.
Fuel can mix with soot to clog the injector.
The air filter is full.
The DOC needs air when it ramps up to go through regen. If the air filter is full or clogged, the DOC can’t get air.


